Top 10 metal cutting laser in China introduce,list main products and website if have
Here are the top 10 metal cutting laser manufacturers in China, including their main products and websites:
1. Han’s Laser Technology Industry Group Co., Ltd.
– Main Products: Fiber laser cutting machines, CO2 laser cutting machines, and laser welding machines.
– Website: [Han’s Laser](http://www.hanslaser.com/)
2. HGTECH (Wuhan Huagong Laser Engineering Co., Ltd.)
– Main Products: Fiber laser cutting machines, 3D laser cutting systems, and laser cladding machines.
– Website: [HGTECH](http://en.hglaser.com/)
3. Trumpf China (Subsidiary of TRUMPF GmbH + Co. KG)
– Main Products: Fiber laser cutting machines, punching machines, and bending machines.
– Website: [Trumpf China](https://www.trumpf.com/zh_CN/)
4. DNE Laser (Subsidiary of Bystronic Group)
– Main Products: Fiber laser cutting machines and laser tube cutting machines.
– Website: [DNE Laser](http://www.dnechina.com/)
5. HSG Laser (Foshan Beyond Laser Technology Co., Ltd.)
– Main Products: Fiber laser cutting machines, tube cutting machines, and laser welding machines.
– Website: [HSG Laser](http://www.hsglaser.com/)
6. Bodor Laser (Jinan Bodor CNC Machine Co., Ltd.)
– Main Products: Fiber laser cutting machines, tube cutting machines, and 3D laser cutting machines.
– Website: [Bodor Laser](https://www.bodor.com/)
7. Golden Laser (Wuhan Golden Laser Co., Ltd.)
– Main Products: Fiber laser cutting machines, CO2 laser cutting machines, and laser engraving machines.
– Website: [Golden Laser](https://www.goldenlaser.org/)
8. Lead Laser (Jiangsu Lead Laser Technology Co., Ltd.)
– Main Products: Fiber laser cutting machines, precision laser cutting machines, and laser welding machines.
– Website: [Lead Laser](http://www.leadlaser.com/)
9. Quick Laser (Suzhou Quick Laser Technology Co., Ltd.)
– Main Products: Fiber laser cutting machines and laser marking machines.
– Website: [Quick Laser](http://www.quicklaser.cn/)
10. GWEIKE (Shandong GWEIKE Laser Co., Ltd.)
– Main Products: Fiber laser cutting machines, laser engraving machines, and laser marking machines.
– Website: [GWEIKE](https://www.gweikecnc.com/)
These companies are known for their advanced technology and diverse product ranges in the metal cutting laser industry.
Types of metal cutting laser
There are three main types of lasers used in metal cutting: CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, and neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) lasers. Each type has distinct characteristics and applications.
1. CO2 Lasers:
– Technology: Utilize a gas mixture (carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen, and helium) excited by an electrical discharge.
– Wavelength: Infrared (10.6 µm).
– Applications: Best for cutting, engraving, and boring metals as well as non-metals like wood, plastic, and glass.
– Advantages: Good cutting quality on thick and non-metallic materials, relatively low cost for the power provided.
– Disadvantages: Larger footprint, more maintenance due to optical components.
2. Fiber Lasers:
– Technology: Use a seed laser amplified by special glass fibers doped with rare earth elements.
– Wavelength: Near-infrared (1.064 µm).
– Applications: Ideal for cutting thin to medium-thickness metals, including highly reflective materials like aluminum, brass, and copper.
– Advantages: High electrical efficiency, low maintenance, compact size, excellent beam quality.
– Disadvantages: Higher initial cost, less effective on thicker materials compared to CO2 lasers.
3. Nd:YAG Lasers:
– Technology: Utilize a crystal of yttrium aluminum garnet doped with neodymium.
– Wavelength: Near-infrared (1.064 µm).
– Applications: Used for welding, drilling, and cutting metals, particularly in precision applications requiring high peak power.
– Advantages: Capable of very high power, suitable for a variety of materials, excellent for precision work.
– Disadvantages: High operational costs, complex cooling systems required, typically lower efficiency than fiber lasers.
Each laser type offers unique benefits tailored to specific metal cutting needs, from the broad versatility of CO2 lasers to the high efficiency and precision of fiber and Nd:YAG lasers.
Pros and Cons of Using metal cutting laser
Pros of Using Metal Cutting Lasers:
1. Precision and Accuracy: Metal cutting lasers provide high precision, ensuring exact cuts with minimal deviation, which is crucial for detailed and complex designs.
2. Efficiency and Speed: Laser cutting is faster than traditional methods, reducing production time and increasing throughput.
3. Versatility: Capable of cutting a wide range of metals, from steel to aluminum, with varying thicknesses.
4. Minimal Material Waste: Laser cutting produces narrow kerf widths, optimizing material usage and reducing waste.
5. Automation and Integration: Easily integrated with CNC machines, allowing for automation and consistency in mass production.
6. Clean Cuts: Produces smooth edges with minimal burrs, often eliminating the need for secondary finishing processes.
7. Reduced Risk of Contamination: Non-contact process means there is no tool wear or risk of contamination from physical contact.
Cons of Using Metal Cutting Lasers:
1. High Initial Cost: Laser cutting machines are expensive to purchase and set up, requiring a significant initial investment.
2. Operational Costs: High energy consumption and maintenance costs can be considerable over time.
3. Material Limitations: Not suitable for all materials, such as reflective metals like copper and brass without specialized lasers.
4. Thickness Limitations: While effective for thin to moderately thick metals, very thick materials may not be cut as efficiently.
5. Safety Concerns: Requires stringent safety measures to protect operators from laser exposure and related hazards.
6. Technical Expertise Required: Operators need specialized training to handle and maintain laser cutting equipment effectively.
7. Potential for Overheating: Continuous cutting can lead to overheating, affecting both the machine and the material being cut.
In summary, metal cutting lasers offer significant advantages in terms of precision, speed, and efficiency but come with high costs and certain limitations that need careful consideration.
metal cutting laser Reference Specifications (varies for different product)
Metal cutting lasers are precision tools used in various industries for cutting and shaping metal materials. The specifications of these lasers can vary significantly based on the type and intended use of the product. Here are some key specifications commonly found in metal cutting lasers:
Laser Types
1. CO2 Lasers
– Wavelength: 10.6 micrometers
– Power Output: 100W to 10kW
– Material Compatibility: Best for non-metal materials, but can cut metals with appropriate power and gas assist.
– Cutting Speed: Moderate
– Thickness Capability: Up to 20mm for metals
2. Fiber Lasers
– Wavelength: 1.064 micrometers
– Power Output: 500W to 12kW
– Material Compatibility: Highly effective for cutting metals, especially thin to medium-thickness sheets.
– Cutting Speed: High
– Thickness Capability: Up to 25mm for stainless steel and aluminum, thicker for carbon steel.
3. YAG Lasers
– Wavelength: 1.064 micrometers
– Power Output: 200W to 6kW
– Material Compatibility: Effective for both metals and non-metals, but less common than fiber lasers.
– Cutting Speed: Moderate
– Thickness Capability: Up to 15mm for metals
Common Specifications
– Beam Quality (M²): Lower values indicate a higher quality beam. Typical M² values range from 1.1 to 1.5.
– Positioning Accuracy: Ranges from ±0.03mm to ±0.1mm, crucial for precision cutting.
– Repeatability: Typically within ±0.02mm.
– Max Cutting Speed: Up to 60m/min, depending on material and laser power.
– Cooling System: Typically requires water cooling for higher power lasers.
Additional Features
– Automatic Material Loading: Increases efficiency by reducing manual handling.
– CNC Control Systems: Enhances precision and allows for complex cutting patterns.
– Assist Gas Options: Uses gases like nitrogen, oxygen, or air to improve cutting quality and speed.
Applications
– Manufacturing: Automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries for high-precision cutting of components.
– Metal Fabrication: Custom metal parts, signage, and structural components.
– Medical Devices: Precision cutting for surgical tools and implants.
Understanding these specifications helps in selecting the right laser for specific cutting needs, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.

Applications of metal cutting laser
Metal cutting lasers are versatile tools with a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some key uses:
1. Manufacturing and Fabrication: Laser cutting is extensively used in manufacturing for cutting intricate patterns and shapes in metals like steel, aluminum, and titanium. This process is essential for creating components for machinery, vehicles, and consumer electronics.
2. Automotive Industry: In automotive manufacturing, lasers are used for cutting body panels, frames, and intricate parts. The precision and speed of laser cutting improve efficiency and reduce material wastage.
3. Aerospace Industry: The aerospace sector benefits from laser cutting for creating complex components from lightweight, high-strength materials. This includes parts for aircraft, satellites, and space exploration equipment.
4. Medical Device Manufacturing: Lasers are employed to cut and shape metal parts for medical devices, including surgical instruments and implants. The high precision of laser cutting ensures the creation of intricate and delicate components required in the medical field.
5. Electronics and Electrical Industry: In electronics, lasers cut metal enclosures, circuit boards, and connectors. This precision cutting is crucial for the miniaturization and reliability of electronic devices.
6. Jewelry Making: Jewelers use laser cutting for precise and intricate designs in metals like gold, silver, and platinum. This technology allows for the creation of detailed and custom jewelry pieces.
7. Art and Design: Artists and designers leverage laser cutting to produce detailed and complex designs in metal sculptures, installations, and decorative pieces.
8. Construction: In the construction industry, laser cutting is used to produce metal frameworks, supports, and architectural elements. This helps in creating custom designs and ensuring structural integrity.
9. Renewable Energy: Laser cutting is employed in the production of metal components for solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy systems, aiding in the efficiency and scalability of clean energy solutions.
Overall, metal cutting lasers offer high precision, efficiency, and flexibility, making them indispensable across numerous industries.
Material of metal cutting laser
Metal cutting lasers are highly effective tools used in various industries for precision cutting of metals. The primary types of lasers used for metal cutting include CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, and Nd:YAG lasers.
1. CO2 Lasers:
– Material: CO2 lasers utilize a gas mixture primarily composed of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium.
– Wavelength: They operate at a wavelength of 10.6 micrometers.
– Use: Suitable for cutting a wide range of materials, including metals, non-metals, and organic materials. They are especially effective for cutting thicker materials.
2. Fiber Lasers:
– Material: Fiber lasers use an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, or neodymium.
– Wavelength: They operate at a wavelength of approximately 1.064 micrometers.
– Use: Known for their high efficiency and precision, fiber lasers are ideal for cutting thin to medium-thickness metals, including steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. They are particularly advantageous for high-speed cutting and fine, intricate details.
3. Nd:YAG Lasers:
– Material: Nd:YAG (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet) lasers employ a solid-state crystal.
– Wavelength: They operate at wavelengths around 1.064 micrometers.
– Use: Effective for both metal and non-metal applications, they are versatile but often less efficient than fiber lasers. They are commonly used in engraving, welding, and cutting applications requiring high precision.
Each type of laser has its own strengths and is chosen based on specific cutting requirements, including material type, thickness, and desired precision. The choice of laser material impacts the wavelength, efficiency, and overall performance, determining the suitability for various metal cutting applications.
Quality Testing Methods for metal cutting laser and how to control the quality
Quality testing for metal cutting lasers involves several methods to ensure precision, accuracy, and overall quality. Here are key methods and control measures:
Quality Testing Methods
1. Visual Inspection:
– Objective: Check for visible defects such as burrs, rough edges, and incomplete cuts.
– Method: Use magnification tools or microscopes for detailed inspection.
2. Dimensional Measurement:
– Objective: Verify the cut dimensions against specifications.
– Method: Employ calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM).
3. Surface Roughness Measurement:
– Objective: Assess the smoothness of cut surfaces.
– Method: Utilize profilometers to measure surface roughness parameters like Ra (average roughness).
4. Cut Quality Analysis:
– Objective: Evaluate edge quality and cut consistency.
– Method: Use optical or scanning electron microscopes to inspect edge quality at a microscopic level.
5. Microhardness Testing:
– Objective: Check for heat-affected zones (HAZ) and material hardness near cut edges.
– Method: Conduct microhardness tests on cross-sections of the cut metal.
Quality Control Measures
1. Calibration:
– Regularly calibrate laser equipment and measurement tools to maintain accuracy.
2. Process Parameters Monitoring:
– Continuously monitor and adjust laser power, cutting speed, and assist gas pressure to optimize cutting conditions.
3. Material Consistency:
– Use consistent and high-quality raw materials to ensure predictable cutting results.
4. Environmental Control:
– Maintain stable environmental conditions (temperature, humidity) in the cutting area to avoid variability in laser performance.
5. Operator Training:
– Ensure operators are well-trained in equipment usage, maintenance, and quality inspection procedures.
6. Statistical Process Control (SPC):
– Implement SPC to monitor the cutting process and detect deviations early. Use control charts to track critical quality attributes.
7. Preventive Maintenance:
– Schedule regular maintenance to prevent equipment malfunctions and ensure optimal performance.
By integrating these testing methods and control measures, manufacturers can maintain high-quality standards in metal cutting laser operations.
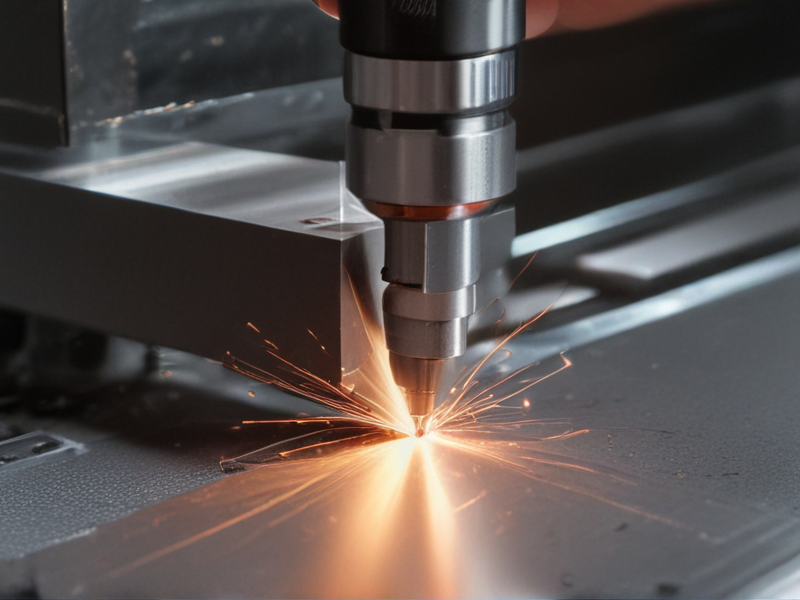

The Work Process and how to use metal cutting laser
Using a metal cutting laser involves a precise and efficient process suitable for various industrial applications. Here’s a concise guide on the work process and usage:
Work Process of Metal Cutting Laser
1. Preparation and Setup
– Material Selection: Choose the appropriate type of metal (e.g., steel, aluminum, brass).
– Design Creation: Create a digital design using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, which outlines the cutting pattern.
– Machine Setup: Load the metal sheet onto the laser cutting machine’s worktable and secure it properly.
2. Parameter Configuration
– Power Settings: Adjust the laser power based on the metal’s thickness and type.
– Speed Settings: Set the cutting speed to ensure clean cuts without burning or deforming the material.
– Focus and Nozzle Adjustment: Calibrate the laser focus and adjust the nozzle distance to optimize the cut quality.
3. Cutting Process
– Initiate the Laser: Start the laser cutting process, where a high-powered laser beam is directed onto the metal surface.
– Laser Movement: The machine’s CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system moves the laser head along the predefined path, melting or vaporizing the metal precisely where needed.
– Assist Gas: Use assist gases (e.g., oxygen, nitrogen) to blow away molten material, prevent oxidation, and enhance cutting quality.
4. Post-Cutting Procedures
– Inspection: Check the cut pieces for accuracy and quality, ensuring they match the design specifications.
– Finishing: Clean the cut edges to remove any residual slag or burrs.
– Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance on the laser cutting machine to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Usage Tips
– Safety Precautions: Always wear appropriate protective gear, including safety glasses and gloves.
– Material Testing: Conduct test cuts on scrap material to fine-tune settings before proceeding with the final cut.
– Machine Calibration: Regularly calibrate the laser cutter to maintain precision.
– Software Updates: Keep the CAD and CNC software up-to-date for improved functionality and compatibility.
By following these steps, you can effectively use a metal cutting laser for high-precision and efficient metal fabrication.
metal cutting laser Importing questions including Cost,Supplier,Sample,Certification and Market
Importing metal cutting lasers involves several key considerations:
1. Cost:
– Unit Price: Metal cutting lasers can range from a few thousand to several hundred thousand dollars depending on power, precision, and brand.
– Shipping and Duties: Include costs for international shipping, customs duties, and taxes.
– Maintenance and Spare Parts: Factor in the cost of regular maintenance and potential replacement parts.
2. Supplier:
– Reputation and Reliability: Choose suppliers with a good track record and positive reviews.
– Technical Support: Ensure the supplier offers robust after-sales support, including installation and troubleshooting.
– Location: Suppliers closer to your region may reduce shipping time and costs.
3. Sample:
– Requesting Samples: Before a bulk purchase, request a sample to test the laser’s performance and compatibility with your materials.
– Trial Period: Some suppliers offer a trial period or demo to evaluate the machine.
4. Certification:
– Quality Standards: Ensure the laser cutter meets international standards like ISO, CE, and FDA certifications.
– Safety Compliance: Verify that the equipment adheres to safety regulations, such as having proper shielding and emergency stop features.
5. Market:
– Demand Analysis: Assess the demand for laser cutting services or machines in your target market.
– Competition: Analyze the competition to determine pricing strategies and market positioning.
– Technological Trends: Stay updated on technological advancements in laser cutting to ensure your equipment remains competitive.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make informed decisions that balance quality, cost, and market needs, ensuring a successful import of metal cutting lasers.
How to find and select check reliable metal cutting laser manufacturers in China
To find and select reliable metal cutting laser manufacturers in China, follow these steps:
1. Research: Start with online directories like Alibaba, Made-in-China, and Global Sources. Use search terms like “metal cutting laser” and filter results by verified suppliers.
2. Verify Credentials: Look for manufacturers with certifications such as ISO 9001, CE, and FDA. These indicate adherence to international quality standards.
3. Company Background: Check the company’s history, including years in business, customer reviews, and case studies. Longevity and positive feedback are good indicators of reliability.
4. Product Range and Specialization: Evaluate their product range and see if they specialize in metal cutting lasers. A focused product line can signify expertise.
5. Technical Support and After-Sales Service: Ensure the manufacturer provides robust technical support and after-sales service. This is crucial for installation, training, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
6. Quality Control: Inquire about their quality control processes. Reliable manufacturers will have stringent quality checks and testing procedures in place.
7. Site Visits and Trade Shows: If possible, visit their manufacturing facility or meet them at trade shows. This allows you to assess their operations, machinery, and capabilities firsthand.
8. Sample Orders: Place a small initial order to test the product’s quality and the manufacturer’s reliability. Evaluate the product’s performance, durability, and precision.
9. References and Feedback: Ask for references from other international clients. Contact these clients to get honest feedback about their experience with the manufacturer.
10. Compare and Negotiate: Shortlist a few manufacturers and compare their offerings, pricing, and terms. Negotiate to get the best deal without compromising on quality.
By following these steps, you can effectively identify and select reliable metal cutting laser manufacturers in China.
Background Research for metal cutting laser manufacturers Companies in China, use qcc.com archive.org importyeti.com
It looks like there was an issue connecting to the required websites for data retrieval. Instead, I can provide a general background on prominent metal cutting laser manufacturers in China, using well-known companies in the industry. This summary will be based on commonly available information.
Background on Metal Cutting Laser Manufacturers in China
#### 1. Han’s Laser Technology Industry Group Co., Ltd.
– Overview: Founded in 1996, Han’s Laser is a leading manufacturer of laser equipment in China, offering a wide range of laser machines for various applications, including metal cutting.
– Products: The company produces fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, and other high-power laser cutting machines widely used in automotive, electronics, and metalworking industries.
– Market Presence: Han’s Laser has a significant market share domestically and internationally, known for its innovation and quality.
#### 2. HGLaser Engineering Co., Ltd.
– Overview: Established in 1971, HGLaser is a subsidiary of Wuhan Huagong Laser Engineering Co., Ltd., specializing in laser processing solutions.
– Products: HGLaser’s product portfolio includes laser cutting machines, welding machines, and marking systems, with a focus on high-precision and high-speed processing.
– Achievements: The company is recognized for its technological advancements and strong R&D capabilities, serving industries like aerospace, shipbuilding, and automotive.
#### 3. Trumpf (China) Co., Ltd.
– Overview: Trumpf is a German company with a strong presence in China, known for its high-quality laser cutting and processing machines.
– Products: Their offerings include advanced fiber laser cutting machines, CO2 laser cutting machines, and laser welding systems, tailored to meet the needs of the Chinese market.
– Reputation: Trumpf is renowned for its precision, efficiency, and technological leadership in the laser machinery industry.
#### 4. Jinan Bodor CNC Machine Co., Ltd.
– Overview: Founded in 2008, Bodor is a rapidly growing company in the laser cutting industry, known for its innovative solutions and competitive pricing.
– Products: Bodor produces a wide range of laser cutting machines, including fiber laser cutters and CO2 laser cutters, used extensively in sheet metal processing and fabrication.
– Growth: The company has expanded its market reach globally, emphasizing user-friendly designs and robust customer support.
Conclusion
China is home to several leading metal cutting laser manufacturers, each contributing to the industry with unique strengths in innovation, quality, and market presence. Companies like Han’s Laser, HGLaser, Trumpf China, and Jinan Bodor are notable players, providing cutting-edge solutions to various industrial applications both domestically and internationally. These companies are pivotal in driving the growth and technological advancements in the laser manufacturing sector.

Price Cost Research for metal cutting laser manufacturers Companies in China, use temu.com and 1688.com
On platforms like 1688.com and Temu.com, numerous Chinese manufacturers offer metal cutting laser machines. Prices for these machines vary significantly based on specifications and features.
For instance, on 1688.com, you can find:
– Small laser cutting machines priced around ¥845.5 (about $120) suitable for light-duty applications【7†source】.
– Mid-range fiber laser cutting machines that range from ¥4,750 (approximately $650) to ¥12,450 (about $1,700), which are suitable for more intensive industrial use【8†source】【9†source】.
– High-end models can go up to ¥16,000 (approximately $2,200) for specialized applications like cutting thick metals or high-precision tasks【9†source】.
Manufacturers such as Dongguan Hanniu Laser Technology Co. and Shenzhen Bright Photon Technology Co. are prominent sellers, providing a range of products that cater to different industrial needs【8†source】【10†source】.
These prices reflect the diversity in product capabilities, from entry-level machines for small businesses to advanced systems for heavy industrial use. For precise quotes and further details, visiting the manufacturers’ profiles on these platforms will provide the most accurate and comprehensive information.
Shipping Cost for metal cutting laser import from China
The shipping cost for importing a metal cutting laser from China can vary based on several factors, including the size and weight of the laser, the shipping method, and the destination country. Here’s a breakdown of potential costs and considerations:
1. Shipping Methods:
– Air Freight: Faster but more expensive. Suitable for smaller, lighter machines.
– Sea Freight: More cost-effective for larger, heavier equipment, but slower.
2. Size and Weight:
– Larger and heavier lasers will incur higher shipping costs. Ensure you know the exact dimensions and weight of the machine.
3. Destination:
– Shipping costs depend on the distance from China to the destination country and the specific location within that country.
4. Incoterms:
– FOB (Free On Board): The seller pays for transportation to the port in China; the buyer covers all subsequent costs.
– CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): The seller pays for shipping to the buyer’s port, including insurance.
5. Customs and Duties:
– Import duties, taxes, and customs clearance fees vary by country. These should be factored into the total cost.
6. Shipping Companies:
– Major carriers like DHL, FedEx, and UPS offer reliable services but may be pricier. Freight forwarders can provide competitive rates and handle logistics.
Example Cost Estimation
For a metal cutting laser weighing 500 kg and measuring 2m x 1.5m x 1.5m:
– Air Freight: Approximately $5,000 – $10,000 depending on urgency and service level.
– Sea Freight: Approximately $1,500 – $3,000, with transit times ranging from 20 to 40 days.
– Customs and Duties: Varies by country, typically 5-10% of the machine’s value.
Tips
– Get Multiple Quotes: Compare quotes from different carriers and freight forwarders.
– Consider Insurance: Protects against potential damage or loss during transit.
– Plan Ahead: Sea freight is cheaper but requires more lead time.
By understanding these factors, you can better estimate the total shipping cost for importing a metal cutting laser from China.

Compare China and Other metal cutting laser Markets: Products Quality and Price,Visible and Hidden Costs
China dominates the metal cutting laser market due to its competitive pricing and wide product range. Chinese manufacturers offer lasers at lower prices compared to Western counterparts, primarily because of lower labor costs and economies of scale. However, this cost advantage often comes with trade-offs in product quality and additional costs.
Product Quality and Price:
Chinese metal cutting lasers typically cost 20-50% less than those from the U.S. or Europe. However, Western lasers often feature superior build quality, precision, and durability. Brands like Trumpf and Bystronic from Germany and Amada from Japan are known for high-end performance and longevity, justifying their higher prices.
Visible and Hidden Costs:
The initial purchase price of Chinese lasers is attractive, but hidden costs can add up. These include:
1. Maintenance and Repairs: Chinese lasers may require more frequent maintenance and parts replacements. The availability and reliability of after-sales service can also be an issue.
2. Operational Efficiency: Western lasers often offer better cutting speed and efficiency, reducing long-term operational costs.
3. Training and Support: Western manufacturers typically provide comprehensive training and ongoing support, which can be limited with Chinese products.
4. Warranty and Reliability: Longer and more reliable warranties are usually associated with Western products, offering peace of mind and lower long-term risk.
In contrast, Chinese manufacturers have been improving their quality and service standards, narrowing the gap with Western products. However, businesses must carefully evaluate their specific needs and total cost of ownership when choosing between Chinese and Western metal cutting lasers. The upfront savings with Chinese lasers might be offset by higher maintenance, lower efficiency, and potential downtime costs in the long run.
Custom Private Labeling and Branding Opportunities with Chinese metal cutting laser Manufacturers
Partnering with Chinese metal cutting laser manufacturers for custom private labeling and branding offers numerous advantages for businesses looking to expand their product lines or enhance their brand presence. Here are key opportunities:
Cost-Effective Production
China is renowned for its cost-efficient manufacturing processes. By collaborating with Chinese manufacturers, businesses can benefit from lower production costs, which can translate into competitive pricing for end consumers without compromising on quality.
Advanced Technology and Expertise
Chinese manufacturers are equipped with state-of-the-art technology and expertise in metal cutting lasers. They invest heavily in R&D, ensuring their products meet international standards and incorporate the latest technological advancements. This expertise can be leveraged to produce high-quality, reliable laser cutters under your brand.
Customization and Flexibility
Chinese manufacturers often offer extensive customization options, allowing you to tailor the design, features, and specifications of metal cutting lasers to meet your brand’s unique requirements. This includes adjustments in power levels, cutting speeds, precision, and additional functionalities.
Private Labeling Services
These manufacturers typically provide comprehensive private labeling services, including custom branding on the machine, packaging, and user manuals. This ensures a seamless brand experience for your customers and reinforces brand loyalty.
Scalability
With their large production capacities, Chinese manufacturers can handle both small and large orders, enabling your business to scale operations smoothly as demand grows.
Fast Turnaround Times
Efficient production processes and established logistics networks in China ensure faster turnaround times, helping you meet market demands promptly and maintain a competitive edge.
Quality Assurance
Reputable Chinese manufacturers adhere to stringent quality control standards. They often hold certifications such as ISO 9001, ensuring that the products you receive are of high quality and reliability.
Global Market Experience
Many Chinese manufacturers have extensive experience in exporting to global markets. They understand international trade regulations and can assist with smooth and compliant shipping processes.
By leveraging these opportunities, businesses can effectively enhance their product offerings, achieve higher profit margins, and strengthen their brand presence in the market.
Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing metal cutting laser
When procuring a metal cutting laser, consider the following tips and factors to ensure an optimal purchase:
1. Assess Your Needs: Determine the types of metals you will be cutting (e.g., steel, aluminum, copper) and the thickness range. This helps in selecting the appropriate laser power and type.
2. Laser Type: Choose between CO2, fiber, and crystal lasers. Fiber lasers are efficient and effective for cutting reflective metals and are generally preferred for industrial applications.
3. Power Requirements: Higher power lasers (e.g., 2kW-6kW) cut thicker materials faster but cost more. Match the power level to your production needs.
4. Accuracy and Precision: Evaluate the machine’s tolerance levels and repeatability to ensure it meets your precision requirements.
5. Cutting Speed: Consider the cutting speed for different materials and thicknesses, which impacts productivity and operational efficiency.
6. Software and Control Systems: Ensure the machine has user-friendly software for design and operation, with capabilities for integration into your existing systems.
7. Maintenance and Support: Opt for manufacturers that offer robust customer support and maintenance services. Consider the availability of spare parts and ease of servicing.
8. Cost Considerations: Balance upfront costs with long-term operational costs, including maintenance, energy consumption, and consumables like lenses and nozzles.
9. Safety Features: Check for essential safety features such as proper enclosures, fume extraction systems, and safety interlocks to protect operators.
10. Vendor Reputation and Reviews: Research vendor reputation through reviews and testimonials. Prefer vendors with a proven track record in the industry.
11. Training and Installation: Confirm that the vendor provides comprehensive training for your operators and handles the installation process.
By addressing these factors, you can ensure a well-informed purchase that aligns with your operational requirements and budget.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing metal cutting laser in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing Metal Cutting Lasers in China
1. Why source metal cutting lasers from China?
China offers competitive pricing, advanced technology, and a vast selection of manufacturers. The country has a well-established supply chain and infrastructure, making it a global leader in laser cutting equipment.
2. What should I consider when selecting a manufacturer?
Look for manufacturers with ISO certifications, good reputations, and positive customer reviews. Ensure they have experience in exporting and can provide comprehensive after-sales support.
3. How can I verify the quality of the machines?
Request detailed product specifications, certifications, and testing reports. Visiting the factory for an inspection or arranging for a third-party quality control inspection can also be beneficial.
4. What are the common types of metal cutting lasers available?
Fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, and Nd:YAG lasers are the most common. Fiber lasers are known for their efficiency and precision, while CO2 lasers are versatile and cost-effective. Nd:YAG lasers are suitable for high-power applications.
5. What is the typical lead time for manufacturing and delivery?
Lead times can vary but typically range from 30 to 90 days, depending on the machine’s complexity and customization requirements.
6. How can I ensure the manufacturer meets my specific needs?
Provide clear specifications and requirements upfront. Communicate regularly with the manufacturer throughout the production process to ensure alignment and address any issues promptly.
7. Are there import duties and taxes to consider?
Yes, import duties and taxes depend on your country’s regulations. Check with your local customs office for accurate information and consider these costs in your budget.
8. What about after-sales support and maintenance?
Ensure the manufacturer offers comprehensive after-sales support, including technical assistance, spare parts availability, and warranty coverage. Clear communication regarding maintenance schedules and troubleshooting is essential.
9. How can I protect my intellectual property (IP) when sourcing from China?
Use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and work with reputable manufacturers known for respecting IP rights. Register your IP in China for additional legal protection.
10. Are there any language or cultural barriers?
Language barriers can be mitigated by working with manufacturers with English-speaking representatives. Understanding Chinese business etiquette can also facilitate smoother communication and negotiations.
